Parallel Transmission And Serial Transmission And Their Advantages
• 3.9.1 Communication • 3.9.1.1 Communication methods • 3.9.1.2 Communication basics Introduction [ ] One of the key aspects of computing is communication. For example, input and output devices need to communicate with the processor, the hard disk needs to communicate with memory and so on. Goat similar game free download in pc. Communication in this sense takes place through the transmission of data and instructions. We have already looked at many examples of data transmission inside the computer. In this section, we are more concerned with communication between computers and peripheral devices and also between one computer and another across local and global networks. This section will also include a detailed analysis of the infrastructure that makes up the Internet.
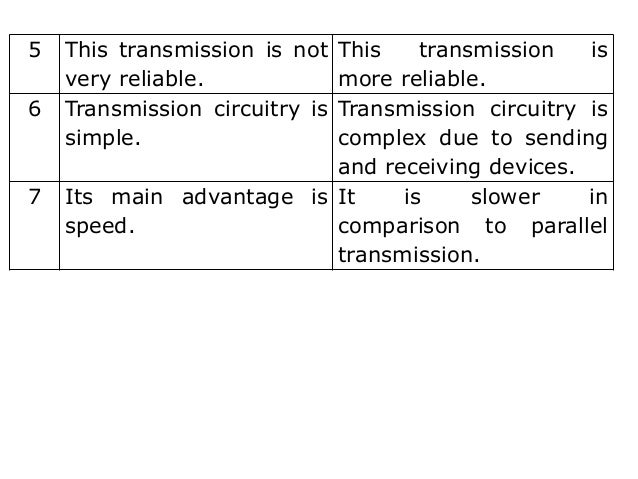
Serial and parallel transmission [ ] Serial transmission [ ]. Serial bit by bit transmission Serial transmission sends and receives data one bit at a time in sequence. Serial connections are used to connect most of the peripherals to the computer such as the mouse and keyboard, and it is serial cables that connect computers together to form a network.
The speed of the transmission will depend on the type of cabling used so it is not necessarily the case that serial transmission is slow. For example, the Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a high-speed serial connection that allows peripheral devices to be connected to your computer. Serial network cables are capable of transmission rates of 1 Gbps (1000 million bits per second). Parallel transmission [ ].
Parallel transmission refers to a situation when binary data transfer occurs simultaneously, while serial transmission refers to one in which binary data transfer occurs one bit at a time. Parallel transmission is faster, but more complicated, because each bit travels along its own data path.
Bandwidth - a measure of the capacity of the channel down which the data is being sent. Measured in hertz (Hz). Bandwidth is the term used to describe the amount of data that can be transmitted along a communication channel. It relates to the range of frequencies that are available on the carrier wave that carries the data.
The range in this case is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies. As the range of frequencies increases so does the amount of data that can be transmitted within the same time frame. We have already touched on the relative speed at which data can be transmitted. Speed is a vital factor in communications.
Bandwidth is measured in hertz (Hz) and megahertz (mHz). Bit rate [ ]. Bit rate - the rate at which data is actually being transmitted. Measured in bits per second. Bit rate is the term used to describe the speed at which a particular transmission is taking place.